C#で強力なパスワードを生成しますか?
C#で強力で安全なパスワードを生成する方法を知りたいと思っていました。
私は少しグーグルしてWikipediaでこの式を見ました。ここで、Lはパスワードの長さ、Nは可能な記号の数です。
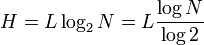
また、私は この質問 を見つけましたが、何らかの理由でメソッドMembership.GeneratePasswordは、1桁の乱数を返すだけで、パスワードはまったくありません。残りのすべてのソリューションは非常に低速でした(> = 0.5秒)。
この数式の実装についてサポートが必要です(どこから始めればよいかわかりません)。別の解決策を提案するか、GeneratePasswordが機能しない理由を説明することもできます。
私はlinqpadで次のことを試しました:
System.Web.Security.Membership.GeneratePassword(25, 10)
これは私が得たパスワードです:
[XTJ_67g.i/ag1rL)6_Yv> * +%
または、それが十分に安全でない場合は、これを試してください:
System.Web.Security.Membership.GeneratePassword(128, 100)
これを3回実行すると、次のようになりました。
| c ^。:?m)#q +(] V;} [Z(})/?-; $] + @!| ^/8 * _9。$&。&!(?= ^!Wx?[@ %+&-@ b;)> N;&+ * w [> $ 2 + _ $%l; + h +#zhs ^ {e?&= *(} X_%|:}]]} * X [+) Er%J /-=; Q0 {:+ =%c7:^ $
/:_)hxF + *){2 |;(>:* N ^ +!_&|} B 。$})?[V = [+ v({-:-@ 9-Z $ j?。[-}(@ MHx +}(} Mz_S(7#4} {..> @ G |!+++ {+ C = | _} = + r ^ @&$ 0; L * | kz-; $ ++/N3 $ =}?;%&]] */^#^!+
:* {]-x ^ $ g {|?*))_ = B @ ^。#%L; g | +)#[nq}?y(_(m;] S ^ I $ * q = l-[_ /?}&-!k ^(+ [_ {Z |&:^%!_)!= p%=)= wYd-#。UP $%s1 {* l%+ [%?! c + 7 = @ = .; {+ M)!^}&d /] {];(&}これは1秒もかかりませんでした。フレームワークはあなたの友達です。
http://msdn.Microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.web.security.membership.generatepassword.aspx を参照してください
その数式に関する質問に対処するには:
この式は、N個の記号のアルファベットから描かれた長さLのパスワードは、two記号のアルファベットから描かれた長さHのパスワードと同等であることを示しています。たとえば、64個の記号(たとえば、abc ... xyzABC ... XYZ01 ... 89_!)があり、パスワードが10文字である場合、パスワードと同等のセキュリティが得られます10 log2 64 = 60文字アルファベット「ab」から引かれた。
「ログ」は、べき乗の逆演算です。 2の6乗は64を与えるので、64の「ログ2」は6を与えます。
私がこれをどこで見つけたかはわかりませんが、ここに、パスワードとして使用できる高エントロピーの真にランダムな文字列を生成するクラスがあります。
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class PasswordGenerator
{
public int MinimumLengthPassword { get; private set; }
public int MaximumLengthPassword { get; private set; }
public int MinimumLowerCaseChars { get; private set; }
public int MinimumUpperCaseChars { get; private set; }
public int MinimumNumericChars { get; private set; }
public int MinimumSpecialChars { get; private set; }
public static string AllLowerCaseChars { get; private set; }
public static string AllUpperCaseChars { get; private set; }
public static string AllNumericChars { get; private set; }
public static string AllSpecialChars { get; private set; }
private readonly string _allAvailableChars;
private readonly RandomSecureVersion _randomSecure = new RandomSecureVersion();
private int _minimumNumberOfChars;
static PasswordGenerator()
{
// Define characters that are valid and reject ambiguous characters such as ilo, IO and 1 or 0
AllLowerCaseChars = GetCharRange('a', 'z', exclusiveChars: "ilo");
AllUpperCaseChars = GetCharRange('A', 'Z', exclusiveChars: "IO");
AllNumericChars = GetCharRange('2', '9');
AllSpecialChars = "!@#%*()$?+-=";
}
public PasswordGenerator(
int minimumLengthPassword = 15,
int maximumLengthPassword = 20,
int minimumLowerCaseChars = 2,
int minimumUpperCaseChars = 2,
int minimumNumericChars = 2,
int minimumSpecialChars = 2)
{
if (minimumLengthPassword < 15)
{
throw new ArgumentException("The minimumlength is smaller than 15.",
"minimumLengthPassword");
}
if (minimumLengthPassword > maximumLengthPassword)
{
throw new ArgumentException("The minimumLength is bigger than the maximum length.",
"minimumLengthPassword");
}
if (minimumLowerCaseChars < 2)
{
throw new ArgumentException("The minimumLowerCase is smaller than 2.",
"minimumLowerCaseChars");
}
if (minimumUpperCaseChars < 2)
{
throw new ArgumentException("The minimumUpperCase is smaller than 2.",
"minimumUpperCaseChars");
}
if (minimumNumericChars < 2)
{
throw new ArgumentException("The minimumNumeric is smaller than 2.",
"minimumNumericChars");
}
if (minimumSpecialChars < 2)
{
throw new ArgumentException("The minimumSpecial is smaller than 2.",
"minimumSpecialChars");
}
_minimumNumberOfChars = minimumLowerCaseChars + minimumUpperCaseChars +
minimumNumericChars + minimumSpecialChars;
if (minimumLengthPassword < _minimumNumberOfChars)
{
throw new ArgumentException(
"The minimum length of the password is smaller than the sum " +
"of the minimum characters of all catagories.",
"maximumLengthPassword");
}
MinimumLengthPassword = minimumLengthPassword;
MaximumLengthPassword = maximumLengthPassword;
MinimumLowerCaseChars = minimumLowerCaseChars;
MinimumUpperCaseChars = minimumUpperCaseChars;
MinimumNumericChars = minimumNumericChars;
MinimumSpecialChars = minimumSpecialChars;
_allAvailableChars =
OnlyIfOneCharIsRequired(minimumLowerCaseChars, AllLowerCaseChars) +
OnlyIfOneCharIsRequired(minimumUpperCaseChars, AllUpperCaseChars) +
OnlyIfOneCharIsRequired(minimumNumericChars, AllNumericChars) +
OnlyIfOneCharIsRequired(minimumSpecialChars, AllSpecialChars);
}
private string OnlyIfOneCharIsRequired(int minimum, string allChars)
{
return minimum > 0 || _minimumNumberOfChars == 0 ? allChars : string.Empty;
}
public string Generate()
{
var lengthOfPassword = _randomSecure.Next(MinimumLengthPassword, MaximumLengthPassword);
// Get the required number of characters of each catagory and
// add random charactes of all catagories
var minimumChars = GetRandomString(AllLowerCaseChars, MinimumLowerCaseChars) +
GetRandomString(AllUpperCaseChars, MinimumUpperCaseChars) +
GetRandomString(AllNumericChars, MinimumNumericChars) +
GetRandomString(AllSpecialChars, MinimumSpecialChars);
var rest = GetRandomString(_allAvailableChars, lengthOfPassword - minimumChars.Length);
var unshuffeledResult = minimumChars + rest;
// Shuffle the result so the order of the characters are unpredictable
var result = unshuffeledResult.ShuffleTextSecure();
return result;
}
private string GetRandomString(string possibleChars, int lenght)
{
var result = string.Empty;
for (var position = 0; position < lenght; position++)
{
var index = _randomSecure.Next(possibleChars.Length);
result += possibleChars[index];
}
return result;
}
private static string GetCharRange(char minimum, char maximum, string exclusiveChars = "")
{
var result = string.Empty;
for (char value = minimum; value <= maximum; value++)
{
result += value;
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(exclusiveChars))
{
var inclusiveChars = result.Except(exclusiveChars).ToArray();
result = new string(inclusiveChars);
}
return result;
}
}
internal static class Extensions
{
private static readonly Lazy<RandomSecureVersion> RandomSecure =
new Lazy<RandomSecureVersion>(() => new RandomSecureVersion());
public static IEnumerable<T> ShuffleSecure<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source)
{
var sourceArray = source.ToArray();
for (int counter = 0; counter < sourceArray.Length; counter++)
{
int randomIndex = RandomSecure.Value.Next(counter, sourceArray.Length);
yield return sourceArray[randomIndex];
sourceArray[randomIndex] = sourceArray[counter];
}
}
public static string ShuffleTextSecure(this string source)
{
var shuffeldChars = source.ShuffleSecure().ToArray();
return new string(shuffeldChars);
}
}
internal class RandomSecureVersion
{
//Never ever ever never use Random() in the generation of anything that requires true security/randomness
//and high entropy or I will hunt you down with a pitchfork!! Only RNGCryptoServiceProvider() is safe.
private readonly RNGCryptoServiceProvider _rngProvider = new RNGCryptoServiceProvider();
public int Next()
{
var randomBuffer = new byte[4];
_rngProvider.GetBytes(randomBuffer);
var result = BitConverter.ToInt32(randomBuffer, 0);
return result;
}
public int Next(int maximumValue)
{
// Do not use Next() % maximumValue because the distribution is not OK
return Next(0, maximumValue);
}
public int Next(int minimumValue, int maximumValue)
{
var seed = Next();
// Generate uniformly distributed random integers within a given range.
return new Random(seed).Next(minimumValue, maximumValue);
}
}
このようにしてコードで消費します:
var generator = new PasswordGenerator();
string password = generator.Generate();
Console.WriteLine(password);
これがあなたに役立つかどうかはわかりませんが、これも強力なランダムパスワードを生成したいときに使用します。すばやく簡単に実装/理解でき、上記のメンバーシッププロバイダーを介したものほど過剰ではありません...
private string Token(byte Length) {
char[] Chars = new char[] {
'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z',
'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9'
};
string String = string.Empty;
Random Random = new Random();
for (byte a = 0; a < Length; a++) {
String += Chars[Random.Next(0, 61)];
};
return (String);
}
配列にいくつかの文字を入力し、それらの数をランダムに選択しないのはなぜですか。それらをグループに分けて、文字番号と特殊文字が含まれていることを確認できます。
また、適切な長さとすべての文字グループのどの程度を含めるかを選択する必要がありますが、それだけです。洗練された数式は必要ないと思います。
ユーザーが生成したパスワードを許可しないシステムの場合、実際には非常に簡単です。どのパスワードも、長いほど安全です。もちろん、モニターなどにポストイットする人は数えません。
おそらく、パスワードが生成される元の文字セットを最大化する必要があります。ただし、生成されるパスワードを制限すると、検索スペースが大幅に減少するため、パスワードをlessで保護します。繰り返しますが、これはユーザーが自分のパスワードを選択できない場合にのみ当てはまります。
生成されたパスワードとユーザーが作成したパスワードの両方を扱う場合、明らかにすべての賭けは無効になります。次に、ユーザーが選択した強力なパスワードに似た、さまざまなクラスのできるだけ多くの文字を使用する方法でパスワードを生成する必要があります。理想的には、ユーザーが作成したパスワードも(存在する場合)渡す必要があるのと同じ制約に準拠する必要があります。
Guid.NewGuid().ToString();はどうですか?
私は自分でGuidを使用します:)。ログイン後にユーザーにパスワードを編集させます。