C ++パフォーマンスの課題:整数からstd :: stringへの変換
誰でも私の整数のパフォーマンスをstd :: stringコードに打ち負かすことができますか?
this one など、C++で整数をstd::stringに変換する方法を説明するいくつかの質問が既にありますが、提供されているソリューションはどれも効率的ではありません。
競合するいくつかの一般的なメソッドのコンパイル可能なコードを次に示します。
- Stringstreamを使用した「C++の方法」: http://ideone.com/jh3Sa
- sO-ersが通常パフォーマンス重視の人に推奨するsprintf: http://ideone.com/82kwR
一般的な信念 に反して、boost::lexical_castには独自の実装があり( 白書 )、stringstreamおよび数値挿入演算子は使用しません。 この他の質問は、それが悲惨であることを示唆している であるため、私はそのパフォーマンスを比較したいのです。
そして、デスクトップコンピューターで競争力のある私自身の貢献は、整数モジュロに依存するアルゴリズムとは異なり、組み込みシステムでも最高速度で実行されるアプローチを示しています。
- ベンのアルゴリズム: http://ideone.com/SsEUW
そのコードを使用したい場合は、単純化されたBSDライセンスで使用できるようにします(商用利用が許可され、帰属表示が必要です)。ただ聞いてください。
最後に、関数ltoaは非標準ですが、広く利用可能です。
- ltoaバージョン、それを提供するコンパイラーを持っている人(ideoneは提供していません): http://ideone.com/T5Wim
回答として、パフォーマンス測定値をすぐに投稿します。
アルゴリズムの規則
- 少なくとも32ビットの符号付きおよび符号なし整数を10進数に変換するコードを提供します。
std::stringとして出力を生成します。- スレッドおよびシグナルと互換性のないトリック(静的バッファーなど)はありません。
- ASCII文字セット。
- 絶対値が表現できない2の補数マシンの
INT_MINでコードをテストしてください。 - 理想的には、出力は
stringstream、 http://ideone.com/jh3Sa を使用する標準C++バージョンと同一の文字である必要がありますが、正しい数も大丈夫です。 - [〜#〜] new [〜#〜]:比較に必要なコンパイラーおよびオプティマイザーのオプション(完全に無効化されているものを除く)を使用できますが、コードは、少なくともVC++ 2010およびg ++でコンパイルし、正しい結果を与える必要もあります。
希望の議論
より良いアルゴリズムに加えて、いくつかの異なるプラットフォームとコンパイラーでベンチマークを取得したいと思います(MB/sスループットを標準の測定単位として使用しましょう)。私のアルゴリズムのコード(sprintfベンチマークはいくつかのショートカットを取ることを知っています-現在修正されています)は、少なくともASCIIの下で、ただし、未定義の動作や出力が無効な入力が見られる場合は、それを指摘してください。
結論:
G ++とVC2010で異なるアルゴリズムが実行されます。これはおそらく、それぞれのstd::stringの実装が異なるためです。 VC2010は明らかにNRVOでより良い仕事をしており、gccでのみ有効な値渡しを取り除くことができます。
sprintfを一桁上回るコードが見つかりました。 ostringstreamは50倍以上遅れます。
チャレンジの勝者はuser434507で、gccで私自身の速度の350%を実行するコードを生成します。 SOコミュニティの気まぐれにより、さらなるエントリは閉じられます。
現在(最終?)のスピードチャンピオンは次のとおりです。
- Gccの場合:user434507、
sprintfの8倍高速: http://ideone.com/0uhhX - Visual C++の場合:Timo、
sprintfの15倍高速: http://ideone.com/VpKO
_#include <string>
const char digit_pairs[201] = {
"00010203040506070809"
"10111213141516171819"
"20212223242526272829"
"30313233343536373839"
"40414243444546474849"
"50515253545556575859"
"60616263646566676869"
"70717273747576777879"
"80818283848586878889"
"90919293949596979899"
};
std::string& itostr(int n, std::string& s)
{
if(n==0)
{
s="0";
return s;
}
int sign = -(n<0);
unsigned int val = (n^sign)-sign;
int size;
if(val>=10000)
{
if(val>=10000000)
{
if(val>=1000000000)
size=10;
else if(val>=100000000)
size=9;
else
size=8;
}
else
{
if(val>=1000000)
size=7;
else if(val>=100000)
size=6;
else
size=5;
}
}
else
{
if(val>=100)
{
if(val>=1000)
size=4;
else
size=3;
}
else
{
if(val>=10)
size=2;
else
size=1;
}
}
size -= sign;
s.resize(size);
char* c = &s[0];
if(sign)
*c='-';
c += size-1;
while(val>=100)
{
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0)
{
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
return s;
}
std::string& itostr(unsigned val, std::string& s)
{
if(val==0)
{
s="0";
return s;
}
int size;
if(val>=10000)
{
if(val>=10000000)
{
if(val>=1000000000)
size=10;
else if(val>=100000000)
size=9;
else
size=8;
}
else
{
if(val>=1000000)
size=7;
else if(val>=100000)
size=6;
else
size=5;
}
}
else
{
if(val>=100)
{
if(val>=1000)
size=4;
else
size=3;
}
else
{
if(val>=10)
size=2;
else
size=1;
}
}
s.resize(size);
char* c = &s[size-1];
while(val>=100)
{
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0)
{
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
return s;
}
_これは、アライメントされていないメモリアクセスを許可しないシステムで爆発します(この場合、*(short*)を介した最初のアライメントされていない割り当てはセグメンテーション違反を引き起こします)。
行うべき重要なことの1つは、_std::string_の使用を最小限にすることです。 (Ironic、私は知っています。)たとえば、Visual Studioでは、コンパイラオプションで/ Ob2を指定しても、std :: stringのメソッドのほとんどの呼び出しはインライン化されません。そのため、std::string::clear()の呼び出しのような些細なことでも、CRTを静的ライブラリとしてリンクする場合は100クロックティック、DLLとしてリンクする場合は300クロッククロックかかります。
同じ理由で、代入、コンストラクタ、デストラクタを回避するため、参照で返す方が優れています。
ああ、ちなみにすごいチャレンジです。これはとても楽しかったです。
送信するアルゴリズムは2つあります(スキップしたい場合は、コードが一番下にあります)。私の比較では、関数が文字列を返し、intおよびunsigned intを処理できることが必要です。文字列を構成しないものとそうでないものを比較しても、実際には意味がありません。
1つ目は、事前に計算されたルックアップテーブルまたは明示的な除算/モジュロを使用しない楽しい実装です。これは、gccおよびmsvc上のTimo以外のすべてと競合しています(以下で説明する正当な理由のため)。 2番目のアルゴリズムは、最高のパフォーマンスを得るための実際の提出です。私のテストでは、gccとmsvcの両方で他のすべてを打ち負かしています。
MSVCの結果のいくつかが非常に良い理由を知っていると思います。 std :: stringには、関連する2つのコンストラクターstd::string(char* str, size_t n)があります
そしてstd::string(ForwardIterator b, ForwardIterator e)
gccは、両方に対して同じことを行います...つまり、2番目を使用して1番目を実装します。最初のコンストラクターは、それよりもはるかに効率的に実装でき、MSVCは実装できます。これの副次的な利点は、場合によっては(私の高速コードやTimoのコードのように)文字列コンストラクターをインライン化できることです。実際、MSVCでこれらのコンストラクターを切り替えるだけで、私のコードはほぼ2倍の差があります。
私のパフォーマンステストの結果:
コードソース:
- ボイス
- Timo
- ergosys
- ser434507
- ser-voigt-timo
- hopman-fun
- hopman-fast
gcc 4.4.5-Ubuntu 10.10 64ビットのO2、Core i5
hopman_fun:124.688 MB /秒--- 8.020 s hopman_fast:137.552 MB /秒--- 7.270 s voigt:120.192 MB /秒--- 8.320 s user_voigt_timo:97.9432 MB /秒--- 10.210 s timo:120.482 MB /秒--- 8.300 s ユーザー:97.7517 MB /秒--- 10.230 s ergosys:101.42 MB /秒--- 9.860 s
Windows 7 64ビット、Core i5上のMSVC 2010 64ビット/ Ox
hopman_fun:127 MB /秒--- 7.874 s hopman_fast:259 MB /秒--- 3.861 s voigt:221.435 MB /秒--- 4.516 s user_voigt_timo:195.695 MB /秒--- 5.110 s timo:253.165 MB /秒--- 3.950 s ユーザー:212.63 MB /秒--- 4.703 s ergosys:78.0518 MB /秒--- 12.812 s
Ideoneの結果とテスト/タイミングフレームワークを次に示します。
http://ideone.com/XZRqp
ideoneは32ビット環境であることに注意してください。私のアルゴリズムは両方ともそれに苦しんでいますが、hopman_fastは少なくともまだ競争力があります。
文字列を作成しない2つ程度の場合には、次の関数テンプレートを追加したことに注意してください。
template <typename T>
std::string itostr(T t) {
std::string ret;
itostr(t, ret);
return ret;
}
今、私のコードのために...まず楽しいもの:
// hopman_fun
template <typename T>
T reduce2(T v) {
T k = ((v * 410) >> 12) & 0x000F000F000F000Full;
return (((v - k * 10) << 8) + k);
}
template <typename T>
T reduce4(T v) {
T k = ((v * 10486) >> 20) & 0xFF000000FFull;
return reduce2(((v - k * 100) << 16) + (k));
}
typedef unsigned long long ull;
inline ull reduce8(ull v) {
ull k = ((v * 3518437209u) >> 45);
return reduce4(((v - k * 10000) << 32) + (k));
}
template <typename T>
std::string itostr(T o) {
union {
char str[16];
unsigned short u2[8];
unsigned u4[4];
unsigned long long u8[2];
};
unsigned v = o < 0 ? ~o + 1 : o;
u8[0] = (ull(v) * 3518437209u) >> 45;
u8[0] = (u8[0] * 28147497672ull);
u8[1] = v - u2[3] * 100000000;
u8[1] = reduce8(u8[1]);
char* f;
if (u2[3]) {
u2[3] = reduce2(u2[3]);
f = str + 6;
} else {
unsigned short* k = u4[2] ? u2 + 4 : u2 + 6;
f = *k ? (char*)k : (char*)(k + 1);
}
if (!*f) f++;
u4[1] |= 0x30303030;
u4[2] |= 0x30303030;
u4[3] |= 0x30303030;
if (o < 0) *--f = '-';
return std::string(f, (str + 16) - f);
}
そして、速いもの:
// hopman_fast
struct itostr_helper {
static unsigned out[10000];
itostr_helper() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
unsigned v = i;
char * o = (char*)(out + i);
o[3] = v % 10 + '0';
o[2] = (v % 100) / 10 + '0';
o[1] = (v % 1000) / 100 + '0';
o[0] = (v % 10000) / 1000;
if (o[0]) o[0] |= 0x30;
else if (o[1] != '0') o[0] |= 0x20;
else if (o[2] != '0') o[0] |= 0x10;
else o[0] |= 0x00;
}
}
};
unsigned itostr_helper::out[10000];
itostr_helper hlp_init;
template <typename T>
std::string itostr(T o) {
typedef itostr_helper hlp;
unsigned blocks[3], *b = blocks + 2;
blocks[0] = o < 0 ? ~o + 1 : o;
blocks[2] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[2] = hlp::out[blocks[2]];
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[1] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[1] = hlp::out[blocks[1]];
blocks[2] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[0] = hlp::out[blocks[0] % 10000];
blocks[1] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
char* f = ((char*)b);
f += 3 - (*f >> 4);
char* str = (char*)blocks;
if (o < 0) *--f = '-';
return std::string(f, (str + 12) - f);
}
質問で提供されるコードのベンチマークデータ:
イデオン(gcc 4.3.4):
- 文字列ストリーム:4.4 MB /秒
- sprintf:25.0 MB /秒
- mine(Ben Voigt) :55.8 MB/s
- Timo :58.5 MB/s
- ser434507 :199 MB/s
- ser434507のBen-Timo-507ハイブリッド :263 MB/s
Core i7、Windows 7 64ビット、8 GB RAM、Visual C++ 2010 32ビット:
cl /Ox /EHsc
- 文字列ストリーム:3.39 MB/s、3.67 MB/s
- sprintf:16.8 MB /秒、16.2 MB /秒
- 鉱山:194 MB/s、207 MB/s(PGOが有効な場合:250 MB/s)
Core i7、Windows 7 64ビット、8 GB RAM、Visual C++ 2010 64ビット:
cl /Ox /EHsc
- 文字列ストリーム:4.42 MB /秒、4.92 MB /秒
- sprintf:21.0 MB /秒、20.8 MB /秒
- 鉱山:238 MB/s、228 MB/s
Core i7、Windows 7 64ビット、8 GB RAM、cygwin gcc 4.3.4:
g++ -O3
- 文字列ストリーム:2.19 MB/s、2.17 MB/s
- sprintf:13.1 MB /秒、13.4 MB /秒
- 鉱山:30.0 MB /秒、30.2 MB /秒
edit:私は自分の答えを追加するつもりでしたが、質問は閉じられたのでここに追加します。 :)私は独自のアルゴリズムを作成し、MSVC 2010でしかテストしていませんでしたが、ベンのコードをかなり改善できました。コード。 -ティモ
Intel Q9450、Win XP 32bit、MSVC 2010
cl /O2 /EHsc
- 文字列ストリーム:2.87 MB/s
- sprintf:16.1 MB /秒
- ベン:202 MB /秒
- Ben(符号なしバッファ):82.0 MB/s
- ergosys(更新バージョン):64.2 MB/s
- ユーザー434507:172 MB/s
- ティモ:241 MB/s
-
const char digit_pairs[201] = {
"00010203040506070809"
"10111213141516171819"
"20212223242526272829"
"30313233343536373839"
"40414243444546474849"
"50515253545556575859"
"60616263646566676869"
"70717273747576777879"
"80818283848586878889"
"90919293949596979899"
};
static const int BUFFER_SIZE = 11;
std::string itostr(int val)
{
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
char *it = &buf[BUFFER_SIZE-2];
if(val>=0) {
int div = val/100;
while(div) {
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*(val-div*100)],2);
val = div;
it-=2;
div = val/100;
}
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*val],2);
if(val<10)
it++;
} else {
int div = val/100;
while(div) {
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[-2*(val-div*100)],2);
val = div;
it-=2;
div = val/100;
}
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[-2*val],2);
if(val<=-10)
it--;
*it = '-';
}
return std::string(it,&buf[BUFFER_SIZE]-it);
}
std::string itostr(unsigned int val)
{
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
char *it = (char*)&buf[BUFFER_SIZE-2];
int div = val/100;
while(div) {
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*(val-div*100)],2);
val = div;
it-=2;
div = val/100;
}
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*val],2);
if(val<10)
it++;
return std::string((char*)it,(char*)&buf[BUFFER_SIZE]-(char*)it);
}
アルゴリズムについてここで得られる情報はかなり素晴らしいものですが、質問は「壊れている」と思うので、なぜそう思うかを説明します。
質問は、int-> std::string変換、およびこれmayは、さまざまなstringstream実装やboost :: lexical_castなどの一般的に利用可能なメソッドを比較するときに重要です。ただし、これを行うために特化したアルゴリズムである新しいコードを要求する場合には意味がありません。理由は、int2stringには常にstd :: stringからのヒープ割り当てが含まれ、変換アルゴリズムの最後の部分を圧縮しようとする場合、これらの測定値をstdによって行われたヒープ割り当てと混合することは理にかなっていないからです: :string。パフォーマンスの変換が必要な場合、私はalways固定サイズのバッファーを使用し、ヒープに何も割り当てません。
要約すると、タイミングを分割する必要があると思います。
- まず、最速(int->固定バッファー)変換。
- 第二に、(固定バッファ-> std :: string)コピーのタイミング。
- 3番目に、コピーを保存するために、std :: string割り当てをバッファとして直接使用する方法を確認します。
これらの側面を1つのタイミング、IMHOで混同しないでください。
私の答えを更新しました... modp_ufast ...
Integer To String Test (Type 1)
[modp_ufast]Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 1.1633sec Rate:206308473.0686nums/sec
[sprintf] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 24.3629sec Rate: 9851045.8556nums/sec
[karma] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 5.2389sec Rate: 45810870.7171nums/sec
[strtk] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 3.3126sec Rate: 72450283.7492nums/sec
[so ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 3.0828sec Rate: 77852152.8820nums/sec
[timo ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 4.7349sec Rate: 50687912.9889nums/sec
[voigt] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 5.1689sec Rate: 46431985.1142nums/sec
[hopman] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 4.6169sec Rate: 51982554.6497nums/sec
Press any key to continue . . .
Integer To String Test(Type 2)
[modp_ufast]Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 0.5072sec Rate:473162716.4618nums/sec
[sprintf] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 22.3483sec Rate: 10739062.9383nums/sec
[karma] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 4.2471sec Rate: 56509024.3035nums/sec
[strtk] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.1683sec Rate:110683636.7123nums/sec
[so ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.7133sec Rate: 88454602.1423nums/sec
[timo ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.8030sec Rate: 85623453.3872nums/sec
[voigt] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 3.4019sec Rate: 70549286.7776nums/sec
[hopman] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.7849sec Rate: 86178023.8743nums/sec
Press any key to continue . . .
Integer To String Test (type 3)
[modp_ufast]Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 1.6482sec Rate:145610315.7819nums/sec
[sprintf] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 20.7064sec Rate: 11590618.6109nums/sec
[karma] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.3036sec Rate: 55767734.3570nums/sec
[strtk] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 2.9297sec Rate: 81919227.9275nums/sec
[so ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 3.0278sec Rate: 79266003.8158nums/sec
[timo ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.0631sec Rate: 59068204.3266nums/sec
[voigt] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.5616sec Rate: 52613393.0285nums/sec
[hopman] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.1248sec Rate: 58184194.4569nums/sec
Press any key to continue . . .
int ufast_utoa10(unsigned int value, char* str)
{
#define JOIN(N) N "0", N "1", N "2", N "3", N "4", N "5", N "6", N "7", N "8", N "9"
#define JOIN2(N) JOIN(N "0"), JOIN(N "1"), JOIN(N "2"), JOIN(N "3"), JOIN(N "4"), \
JOIN(N "5"), JOIN(N "6"), JOIN(N "7"), JOIN(N "8"), JOIN(N "9")
#define JOIN3(N) JOIN2(N "0"), JOIN2(N "1"), JOIN2(N "2"), JOIN2(N "3"), JOIN2(N "4"), \
JOIN2(N "5"), JOIN2(N "6"), JOIN2(N "7"), JOIN2(N "8"), JOIN2(N "9")
#define JOIN4 JOIN3("0"), JOIN3("1"), JOIN3("2"), JOIN3("3"), JOIN3("4"), \
JOIN3("5"), JOIN3("6"), JOIN3("7"), JOIN3("8"), JOIN3("9")
#define JOIN5(N) JOIN(N), JOIN(N "1"), JOIN(N "2"), JOIN(N "3"), JOIN(N "4"), \
JOIN(N "5"), JOIN(N "6"), JOIN(N "7"), JOIN(N "8"), JOIN(N "9")
#define JOIN6 JOIN5(), JOIN5("1"), JOIN5("2"), JOIN5("3"), JOIN5("4"), \
JOIN5("5"), JOIN5("6"), JOIN5("7"), JOIN5("8"), JOIN5("9")
#define F(N) ((N) >= 100 ? 3 : (N) >= 10 ? 2 : 1)
#define F10(N) F(N),F(N+1),F(N+2),F(N+3),F(N+4),F(N+5),F(N+6),F(N+7),F(N+8),F(N+9)
#define F100(N) F10(N),F10(N+10),F10(N+20),F10(N+30),F10(N+40),\
F10(N+50),F10(N+60),F10(N+70),F10(N+80),F10(N+90)
static const short offsets[] = { F100(0), F100(100), F100(200), F100(300), F100(400),
F100(500), F100(600), F100(700), F100(800), F100(900)};
static const char table1[][4] = { JOIN("") };
static const char table2[][4] = { JOIN2("") };
static const char table3[][4] = { JOIN3("") };
static const char table4[][5] = { JOIN4 };
static const char table5[][4] = { JOIN6 };
#undef JOIN
#undef JOIN2
#undef JOIN3
#undef JOIN4
char *wstr;
int remains[2];
unsigned int v2;
if (value >= 100000000) {
v2 = value / 10000;
remains[0] = value - v2 * 10000;
value = v2;
v2 = value / 10000;
remains[1] = value - v2 * 10000;
value = v2;
wstr = str;
if (value >= 1000) {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[value];
wstr += 4;
} else {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table5[value];
wstr += offsets[value];
}
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[1]];
wstr += 4;
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[0]];
wstr += 4;
*wstr = 0;
return (wstr - str);
}
else if (value >= 10000) {
v2 = value / 10000;
remains[0] = value - v2 * 10000;
value = v2;
wstr = str;
if (value >= 1000) {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[value];
wstr += 4;
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[0]];
wstr += 4;
*wstr = 0;
return 8;
} else {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table5[value];
wstr += offsets[value];
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[0]];
wstr += 4;
*wstr = 0;
return (wstr - str);
}
}
else {
if (value >= 1000) {
*(__int32 *) str = *(__int32 *) table4[value];
str += 4;
*str = 0;
return 4;
} else if (value >= 100) {
*(__int32 *) str = *(__int32 *) table3[value];
return 3;
} else if (value >= 10) {
*(__int16 *) str = *(__int16 *) table2[value];
str += 2;
*str = 0;
return 2;
} else {
*(__int16 *) str = *(__int16 *) table1[value];
return 1;
}
}
}
int ufast_itoa10(int value, char* str) {
if (value < 0) { *(str++) = '-';
return ufast_utoa10(-value, str) + 1;
}
else return ufast_utoa10(value, str);
}
void ufast_test() {
print_mode("[modp_ufast]");
std::string s;
s.reserve(32);
std::size_t total_length = 0;
strtk::util::timer t;
t.start();
char buf[128];
int len;
for (int i = (-max_i2s / 2); i < (max_i2s / 2); ++i)
{
#ifdef enable_test_type01
s.resize(ufast_itoa10(((i & 1) ? i : -i), const_cast<char*>(s.c_str())));
total_length += s.size();
#endif
#ifdef enable_test_type02
s.resize(ufast_itoa10(max_i2s + i, const_cast<char*>(s.c_str())));
total_length += s.size();
#endif
#ifdef enable_test_type03
s.resize(ufast_itoa10(randval[(max_i2s + i) & 1023], const_cast<char*>(s.c_str())));
total_length += s.size();
#endif
}
t.stop();
printf("Numbers:%10lu\tTotal:%12lu\tTime:%8.4fsec\tRate:%14.4fnums/sec\n",
static_cast<unsigned long>(3 * max_i2s),
static_cast<unsigned long>(total_length),
t.time(),
(3.0 * max_i2s) / t.time());
}
VSでテストすることはできませんが、これはg ++のコードよりも10%程度速いようです。おそらく調整することができ、選択された決定値は推測です。 intのみ、ごめんなさい。
typedef unsigned buf_t;
static buf_t * reduce(unsigned val, buf_t * stp) {
unsigned above = val / 10000;
if (above != 0) {
stp = reduce(above, stp);
val -= above * 10000;
}
buf_t digit = val / 1000;
*stp++ = digit + '0';
val -= digit * 1000;
digit = val / 100;
*stp++ = digit + '0';
val -= digit * 100;
digit = val / 10;
*stp++ = digit + '0';
val -= digit * 10;
*stp++ = val + '0';
return stp;
}
std::string itostr(int input) {
buf_t buf[16];
if(input == INT_MIN) {
char buf2[16];
std::sprintf(buf2, "%d", input);
return std::string(buf2);
}
// handle negative
unsigned val = input;
if(input < 0)
val = -input;
buf[0] = '0';
buf_t* endp = reduce(val, buf+1);
*endp = 127;
buf_t * stp = buf+1;
while (*stp == '0')
stp++;
if (stp == endp)
stp--;
if (input < 0) {
stp--;
*stp = '-';
}
return std::string(stp, endp);
}
この楽しいパズルの私の小さな試みはここにあります。
ルックアップテーブルを使用する代わりに、コンパイラがすべてを把握することを望みました。特にこの場合-ハッカーの喜びを読むと、除算とモジュロがどのように機能するかがわかります。これにより、SSE/AVX命令を使用してそれを最適化できます。
パフォーマンスベンチマーク
速度については、ここでのベンチマークでは、Timoの作業よりも1.5倍高速であることがわかります(Intel Haswellでは約1 GB /秒で実行されます)。
チートと考えられるもの
私が使用している「std-a-std-string」チートについては、もちろん、Timoのメソッドのベンチマークについても考慮しました。
私は組み込み関数BSRを使用します。必要に応じて、代わりにDeBruijnテーブルを使用することもできます。これは、「最速の2log」の投稿で書いたものの1つです。もちろん、これにはパフォーマンスのペナルティがあります(*まあ...多くのitoa操作をしている場合、実際に高速なBSRを作成できますが、それは公平ではないと思います...)。
動作方法
最初に行うことは、必要なメモリ量を把握することです。これは基本的に10logであり、多くのスマートな方法で実装できます。詳細については、頻繁に引用される「 Bit Twiddling Hacks 」を参照してください。
次に行うことは、数値出力を実行することです。これにはテンプレートの再帰を使用しているため、コンパイラーはそれを把握します。
私は「modulo」と「div」をすぐ隣で使用しています。 Hacker's Delightを読むと、この2つが密接に関連していることに気付くでしょう。したがって、1つの答えがあれば、おそらくもう1つも答えがあるでしょう。コンパイラーが詳細を把握できると考えました... :-)
コード
(変更された)log10を使用して桁数を取得する:
struct logarithm
{
static inline int log2(unsigned int value)
{
unsigned long index;
if (!_BitScanReverse(&index, value))
{
return 0;
}
// add 1 if x is NOT a power of 2 (to do the ceil)
return index + (value&(value - 1) ? 1 : 0);
}
static inline int numberDigits(unsigned int v)
{
static unsigned int const PowersOf10[] =
{ 0, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000, 10000000, 100000000, 1000000000 };
int t = (logarithm::log2(v) + 1) * 1233 >> 12; // (use a lg2 method from above)
return 1 + t - (v < PowersOf10[t]);
}
};
文字列を取得する:
template <int count>
struct WriteHelper
{
inline static void WriteChar(char* buf, unsigned int value)
{
unsigned int div = value / 10;
unsigned int rem = value % 10;
buf[count - 1] = rem + '0';
WriteHelper<count - 1>::WriteChar(buf, div);
}
};
template <>
struct WriteHelper<1>
{
inline static void WriteChar(char* buf, unsigned int value)
{
buf[0] = '0' + value;
}
};
// Boring code that converts a length into a switch.
// TODO: Test if recursion with an 'if' is faster.
static inline void WriteNumber(char* data, int len, unsigned int val)
{
switch (len) {
case 1:
WriteHelper<1>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 2:
WriteHelper<2>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 3:
WriteHelper<3>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 4:
WriteHelper<4>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 5:
WriteHelper<5>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 6:
WriteHelper<6>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 7:
WriteHelper<7>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 8:
WriteHelper<8>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 9:
WriteHelper<9>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 10:
WriteHelper<10>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
}
}
// The main method you want to call...
static int Write(char* data, int val)
{
int len;
if (val >= 0)
{
len = logarithm::numberDigits(val);
WriteNumber(data, len, unsigned int(val));
return len;
}
else
{
unsigned int v(-val);
len = logarithm::numberDigits(v);
WriteNumber(data+1, len, v);
data[0] = '-';
return len + 1;
}
}
私はこれをしばらくの間座っていて、ついにそれを投稿することに取り掛かりました。
一度にダブルワードと比較していくつかのメソッドhopman_fast。結果はGCCの短い文字列に最適化されたstd :: stringに対するものです。そうしないと、コピーオンライト文字列管理コードのオーバーヘッドによってパフォーマンスの違いが不明瞭になります。スループットは、このトピックの他の部分と同じ方法で測定されます。サイクルカウントは、出力バッファーを文字列にコピーする前のコードの未加工のシリアル化部分に対するものです。
HOPMAN_FAST - performance reference
TM_CPP, TM_VEC - scalar and vector versions of Terje Mathisen algorithm
WM_VEC - intrinsics implementation of Wojciech Mula's vector algorithm
AK_BW - Word-at-a-time routine with a jump table that fills a buffer in reverse
AK_FW - forward-stepping Word-at-a-time routine with a jump table in Assembly
AK_UNROLLED - generic Word-at-a-time routine that uses an unrolled loop
コンパイル時スイッチ:
-DVSTRING-古いGCCセットアップのSSO文字列を有効にします
-DBSR1-高速log10を有効にします
-DRDTSC-サイクルカウンターを有効にします
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <climits>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <limits>
#include <ctime>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
/* Uncomment to run */
// #define HOPMAN_FAST
// #define TM_CPP
// #define TM_VEC
// #define WM_VEC
// #define AK_UNROLLED
// #define AK_BW
// #define AK_FW
using namespace std;
#ifdef VSTRING
#include <ext/vstring.h>
typedef __gnu_cxx::__vstring string_type;
#else
typedef string string_type;
#endif
namespace detail {
#ifdef __GNUC__
#define ALIGN(N) __attribute__ ((aligned(N)))
#define PACK __attribute__ ((packed))
inline size_t num_digits(unsigned u) {
struct {
uint32_t count;
uint32_t max;
} static digits[32] ALIGN(64) = {
{ 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 },
{ 2, 99 }, { 2, 99 }, { 2, 99 },
{ 3, 999 }, { 3, 999 }, { 3, 999 },
{ 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 },
{ 5, 99999 }, { 5, 99999 }, { 5, 99999 },
{ 6, 999999 }, { 6, 999999 }, { 6, 999999 },
{ 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 },
{ 8, 99999999 }, { 8, 99999999 }, { 8, 99999999 },
{ 9, 999999999 }, { 9, 999999999 }, { 9, 999999999 },
{ 10, UINT_MAX }, { 10, UINT_MAX }
};
#if (defined(i386) || defined(__x86_64__)) && (defined(BSR1) || defined(BSR2))
size_t l = u;
#if defined(BSR1)
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"bsrl %k0, %k0 \n\t"
"shlq $32, %q1 \n\t"
"movq %c2(,%0,8), %0\n\t"
"cmpq %0, %q1 \n\t"
"seta %b1 \n\t"
"addl %1, %k0 \n\t"
: "+r" (l), "+r"(u)
: "i"(digits)
: "cc"
);
return l;
#else
__asm__ __volatile__ ( "bsr %0, %0;" : "+r" (l) );
return digits[l].count + ( u > digits[l].max );
#endif
#else
size_t l = (u != 0) ? 31 - __builtin_clz(u) : 0;
return digits[l].count + ( u > digits[l].max );
#endif
}
#else
inline unsigned msb_u32(unsigned x) {
static const unsigned bval[] = { 0,1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,4,4,4,4 };
unsigned base = 0;
if (x & (unsigned) 0xFFFF0000) { base += 32/2; x >>= 32/2; }
if (x & (unsigned) 0x0000FF00) { base += 32/4; x >>= 32/4; }
if (x & (unsigned) 0x000000F0) { base += 32/8; x >>= 32/8; }
return base + bval[x];
}
inline size_t num_digits(unsigned x) {
static const unsigned powertable[] = {
0,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000,10000000,100000000, 1000000000 };
size_t lg_ten = msb_u32(x) * 1233 >> 12;
size_t adjust = (x >= powertable[lg_ten]);
return lg_ten + adjust;
}
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
struct CharBuffer {
class reverse_iterator : public iterator<random_access_iterator_tag, char> {
char* m_p;
public:
reverse_iterator(char* p) : m_p(p - 1) {}
reverse_iterator operator++() { return --m_p; }
reverse_iterator operator++(int) { return m_p--; }
char operator*() const { return *m_p; }
bool operator==( reverse_iterator it) const { return m_p == it.m_p; }
bool operator!=( reverse_iterator it) const { return m_p != it.m_p; }
difference_type operator-( reverse_iterator it) const { return it.m_p - m_p; }
};
};
union PairTable {
char c[2];
unsigned short u;
} PACK table[100] ALIGN(1024) = {
{{'0','0'}},{{'0','1'}},{{'0','2'}},{{'0','3'}},{{'0','4'}},{{'0','5'}},{{'0','6'}},{{'0','7'}},{{'0','8'}},{{'0','9'}},
{{'1','0'}},{{'1','1'}},{{'1','2'}},{{'1','3'}},{{'1','4'}},{{'1','5'}},{{'1','6'}},{{'1','7'}},{{'1','8'}},{{'1','9'}},
{{'2','0'}},{{'2','1'}},{{'2','2'}},{{'2','3'}},{{'2','4'}},{{'2','5'}},{{'2','6'}},{{'2','7'}},{{'2','8'}},{{'2','9'}},
{{'3','0'}},{{'3','1'}},{{'3','2'}},{{'3','3'}},{{'3','4'}},{{'3','5'}},{{'3','6'}},{{'3','7'}},{{'3','8'}},{{'3','9'}},
{{'4','0'}},{{'4','1'}},{{'4','2'}},{{'4','3'}},{{'4','4'}},{{'4','5'}},{{'4','6'}},{{'4','7'}},{{'4','8'}},{{'4','9'}},
{{'5','0'}},{{'5','1'}},{{'5','2'}},{{'5','3'}},{{'5','4'}},{{'5','5'}},{{'5','6'}},{{'5','7'}},{{'5','8'}},{{'5','9'}},
{{'6','0'}},{{'6','1'}},{{'6','2'}},{{'6','3'}},{{'6','4'}},{{'6','5'}},{{'6','6'}},{{'6','7'}},{{'6','8'}},{{'6','9'}},
{{'7','0'}},{{'7','1'}},{{'7','2'}},{{'7','3'}},{{'7','4'}},{{'7','5'}},{{'7','6'}},{{'7','7'}},{{'7','8'}},{{'7','9'}},
{{'8','0'}},{{'8','1'}},{{'8','2'}},{{'8','3'}},{{'8','4'}},{{'8','5'}},{{'8','6'}},{{'8','7'}},{{'8','8'}},{{'8','9'}},
{{'9','0'}},{{'9','1'}},{{'9','2'}},{{'9','3'}},{{'9','4'}},{{'9','5'}},{{'9','6'}},{{'9','7'}},{{'9','8'}},{{'9','9'}}
};
} // namespace detail
struct progress_timer {
clock_t c;
progress_timer() : c(clock()) {}
int elapsed() { return clock() - c; }
~progress_timer() {
clock_t d = clock() - c;
cout << d / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "."
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 1000 / 100)
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 100 / 10)
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 10)
<< " s" << endl;
}
};
#ifdef HOPMAN_FAST
namespace hopman_fast {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
struct itostr_helper {
static ALIGN(1024) unsigned out[10000];
itostr_helper() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
unsigned v = i;
char * o = (char*)(out + i);
o[3] = v % 10 + '0';
o[2] = (v % 100) / 10 + '0';
o[1] = (v % 1000) / 100 + '0';
o[0] = (v % 10000) / 1000;
if (o[0]) o[0] |= 0x30;
else if (o[1] != '0') o[0] |= 0x20;
else if (o[2] != '0') o[0] |= 0x10;
else o[0] |= 0x00;
}
}
};
unsigned itostr_helper::out[10000];
itostr_helper hlp_init;
template <typename T>
string_type itostr(T o) {
typedef itostr_helper hlp;
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
unsigned blocks[3], *b = blocks + 2;
blocks[0] = o < 0 ? ~o + 1 : o;
blocks[2] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[2] = hlp::out[blocks[2]];
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[1] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[1] = hlp::out[blocks[1]];
blocks[2] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[0] = hlp::out[blocks[0] % 10000];
blocks[1] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
char* f = ((char*)b);
f += 3 - (*f >> 4);
char* str = (char*)blocks;
if (o < 0) *--f = '-';
str += 12;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(f, str);
}
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
namespace ak {
#ifdef AK_UNROLLED
namespace unrolled {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static const size_t MaxValueSize = 16;
static inline char* generate(int value, char* buffer) {
union { char* pc; unsigned short* pu; } b = { buffer + MaxValueSize };
unsigned u, v = value < 0 ? unsigned(~value) + 1 : value;
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
} } } }
*(b.pc -= (u >= 10)) = '-';
return b.pc + (value >= 0);
}
static inline char* generate(unsigned value, char* buffer) {
union { char* pc; unsigned short* pu; } b = { buffer + MaxValueSize };
unsigned u, v = value;
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
} } } }
return b.pc + (u < 10);
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(value_type v) {
char buf[MaxValueSize];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char* p = generate(v, buf);
char* e = buf + MaxValueSize;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(p, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#if defined(AK_BW)
namespace bw {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
typedef uint64_t u_type;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, size_t len, char* buffer) {
u_type u = v;
switch(len) {
default: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 8) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 8: v = (u * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 6) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 6: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 4) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 4: v = (u * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 2) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 2: *(uint16_t*)buffer = detail::table[v].u;
case 0: return;
case 9: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 7) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 7: v = (u * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 5) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 5: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 3) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 3: v = (u * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 1) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 1: *buffer = v + 0x30;
}
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
buf[0] = '-';
char* e = buf + neg;
generate(val, len, e);
e += len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#if defined(AK_FW)
namespace fw {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
typedef uint32_t u_type;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, size_t len, char* buffer) {
#if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__x86_64__)
uint16_t w;
uint32_t u;
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"jmp %*T%=(,%3,8) \n\t"
"T%=: .quad L0%= \n\t"
" .quad L1%= \n\t"
" .quad L2%= \n\t"
" .quad L3%= \n\t"
" .quad L4%= \n\t"
" .quad L5%= \n\t"
" .quad L6%= \n\t"
" .quad L7%= \n\t"
" .quad L8%= \n\t"
" .quad L9%= \n\t"
" .quad L10%= \n\t"
"L10%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1441151881, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $57, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, (%4) \n\t"
"L8%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1125899907, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $50, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $1000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -8(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L6%=: \n\t"
" imulq $429497, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $32, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $10000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -6(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L4%=: \n\t"
" imull $167773, %0, %1 \n\t"
" shrl $24, %1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -4(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L2%=: \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q0,2), %w2 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -2(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L0%=: jmp 1f \n\t"
"L9%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1801439851, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $54, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $10000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, (%4) \n\t"
"L7%=: \n\t"
" imulq $43980466, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $42, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -7(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L5%=: \n\t"
" imulq $268436, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $28, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $1000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -5(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L3%=: \n\t"
" imull $6554, %0, %1 \n\t"
" shrl $15, %1 \n\t"
" andb $254, %b1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1), %w2 \n\t"
" leal (%1,%1,4), %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -3(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L1%=: \n\t"
" addl $48, %0 \n\t"
" movb %b0, -1(%4,%3) \n\t"
"1: \n\t"
: "+r"(v), "=&q"(u), "=&r"(w)
: "r"(len), "r"(buffer), "i"(detail::table)
: "memory", "cc"
);
#else
u_type u;
switch(len) {
default: u = (v * 1441151881ULL) >> 57; *(uint16_t*)(buffer) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100000000;
case 8: u = (v * 1125899907ULL) >> 50; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 8) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 1000000;
case 6: u = (v * 429497ULL) >> 32; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 6) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10000;
case 4: u = (v * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 4) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100;
case 2: *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 2) = detail::table[v].u;
case 0: return;
case 9: u = (v * 1801439851ULL) >> 54; *(uint16_t*)(buffer) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10000000;
case 7: u = (v * 43980466ULL) >> 42; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 7) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100000;
case 5: u = (v * 268436ULL) >> 28; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 5) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 1000;
case 3: u = (v * 6554) >> 16; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 3) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10;
case 1: *(buffer + len - 1) = v + 0x30;
}
#endif
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
if (neg) buf[0] = '-';
char* e = buf + len + neg;
generate(val, len, buf + neg);
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
} // ak
namespace wm {
#ifdef WM_VEC
#if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__x86_64__)
namespace vec {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline unsigned generate(unsigned v, char* buf) {
static struct {
unsigned short mul_10[8];
unsigned short div_const[8];
unsigned short shl_const[8];
unsigned char to_ascii[16];
} ALIGN(64) bits =
{
{ // mul_10
10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10
},
{ // div_const
8389, 5243, 13108, 0x8000, 8389, 5243, 13108, 0x8000
},
{ // shl_const
1 << (16 - (23 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - (19 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - 1 - 2),
1 << (15),
1 << (16 - (23 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - (19 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - 1 - 2),
1 << (15)
},
{ // to_ascii
'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0',
'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0'
}
};
unsigned x, y, l;
x = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37;
y = v;
l = 0;
if (x) {
unsigned div = 0xd1b71759;
unsigned mul = 55536;
__m128i z, m, a, o;
y -= 100 * x;
z = _mm_cvtsi32_si128(x);
m = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.mul_10);
o = _mm_mul_epu32( z, _mm_cvtsi32_si128(div));
z = _mm_add_epi32( z, _mm_mul_epu32( _mm_cvtsi32_si128(mul), _mm_srli_epi64( o, 45) ) );
z = _mm_slli_epi64( _mm_shuffle_epi32( _mm_unpacklo_epi16(z, z), 5 ), 2 );
a = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.to_ascii);
z = _mm_mulhi_epu16( _mm_mulhi_epu16( z, *(__m128i*)bits.div_const ), *(__m128i*)bits.shl_const );
z = _mm_sub_epi16( z, _mm_slli_epi64( _mm_mullo_epi16( m, z ), 16 ) );
z = _mm_add_epi8( _mm_packus_epi16( z, _mm_xor_si128(o, o) ), a );
x = __builtin_ctz( ~_mm_movemask_epi8( _mm_cmpeq_epi8( a, z ) ) );
l = 8 - x;
uint64_t q = _mm_cvtsi128_si64(z) >> (x * 8);
*(uint64_t*)buf = q;
buf += l;
x = 1;
}
v = (y * 6554) >> 16;
l += 1 + (x | (v != 0));
*(unsigned short*)buf = 0x30 + ((l > 1) ? ((0x30 + y - v * 10) << 8) + v : y);
return l;
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
buf[0] = '-';
unsigned len = generate(val, buf + neg);
char* e = buf + len + neg;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
inline string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
inline string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#endif
} // wm
namespace tmn {
#ifdef TM_CPP
namespace cpp {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, char* buffer) {
unsigned const f1_10000 = (1 << 28) / 10000;
unsigned tmplo, tmphi;
unsigned lo = v % 100000;
unsigned hi = v / 100000;
tmplo = lo * (f1_10000 + 1) - (lo >> 2);
tmphi = hi * (f1_10000 + 1) - (hi >> 2);
unsigned mask = 0x0fffffff;
unsigned shift = 28;
for(size_t i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
buffer[i + 0] = '0' + (char)(tmphi >> shift);
buffer[i + 5] = '0' + (char)(tmplo >> shift);
tmphi = (tmphi & mask) * 5;
tmplo = (tmplo & mask) * 5;
mask >>= 1;
shift--;
}
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char buf[16];
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
char* e = buf + 11;
generate(val, buf + 1);
buf[10 - len] = '-';
len += neg;
char* b = e - len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(b, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#ifdef TM_VEC
namespace vec {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline unsigned generate(unsigned val, char* buffer) {
static struct {
unsigned char mul_10[16];
unsigned char to_ascii[16];
unsigned char gather[16];
unsigned char shift[16];
} ALIGN(64) bits = {
{ 10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0 },
{ '0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0' },
{ 3,5,6,7,9,10,11,13,14,15,0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15 }
};
unsigned u = val / 1000000;
unsigned l = val - u * 1000000;
__m128i x, h, f, m, n;
n = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.mul_10);
x = _mm_set_epi64x( l, u );
h = _mm_mul_epu32( x, _mm_set1_epi32(4294968) );
x = _mm_sub_epi64( x, _mm_srli_epi64( _mm_mullo_epi32( h, _mm_set1_epi32(1000) ), 32 ) );
f = _mm_set1_epi32((1 << 28) / 1000 + 1);
m = _mm_srli_epi32( _mm_cmpeq_epi32(m, m), 4 );
x = _mm_shuffle_epi32( _mm_blend_epi16( x, h, 204 ), 177 );
f = _mm_sub_epi32( _mm_mullo_epi32(f, x), _mm_srli_epi32(x, 2) );
h = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.to_ascii);
x = _mm_srli_epi32(f, 28);
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 8) );
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 16) );
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 24) );
x = _mm_add_epi8( _mm_shuffle_epi8(x, *(__m128i*)bits.gather), h );
l = __builtin_ctz( ~_mm_movemask_epi8( _mm_cmpeq_epi8( h, x ) ) | (1 << 9) );
x = _mm_shuffle_epi8( x, _mm_add_epi8(*(__m128i*)bits.shift, _mm_set1_epi8(l) ) );
_mm_store_si128( (__m128i*)buffer, x );
return 10 - l;
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char arena[32];
char* buf = (char*)((uintptr_t)(arena + 16) & ~(uintptr_t)0xf);
*(buf - 1)= '-';
unsigned len = generate(val, buf) + neg;
buf -= neg;
char* end = buf + len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, end);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
}
bool fail(string in, string_type out) {
cout << "failure: " << in << " => " << out << endl;
return false;
}
#define TEST(x, n) \
stringstream ss; \
string_type s = n::itostr(x); \
ss << (long long)x; \
if (::strcmp(ss.str().c_str(), s.c_str())) { \
passed = fail(ss.str(), s); \
break; \
}
#define test(x) { \
passed = true; \
if (0 && passed) { \
char c = CHAR_MIN; \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while (c++ != CHAR_MAX); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed char!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (0 && passed) { \
short c = numeric_limits<short>::min(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while (c++ != numeric_limits<short>::max()); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed short!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (passed) { \
int c = numeric_limits<int>::min(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while ((c += 100000) < numeric_limits<int>::max() - 100000); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed int!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (passed) { \
unsigned c = numeric_limits<unsigned>::max(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while ((c -= 100000) > 100000); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed unsigned int!!!" << endl; \
} \
}
#define time(x, N) \
if (passed) { \
static const int64_t limits[] = \
{0, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, \
1000000, 10000000, 100000000, 1000000000, 10000000000ULL }; \
long passes = 0; \
cout << #x << ": "; \
progress_timer t; \
uint64_t s = 0; \
if (do_time) { \
for (int n = 0; n < N1; n++) { \
int i = 0; \
while (i < N2) { \
int v = ((NM - i) % limits[N]) | (limits[N] / 10); \
int w = x::itostr(v).size() + \
x::itostr(-v).size(); \
i += w * mult; \
passes++; \
} \
s += i / mult; \
} \
} \
k += s; \
cout << N << " digits: " \
<< s / double(t.elapsed()) * CLOCKS_PER_SEC/1000000 << " MB/sec, " << (x::cycles() / passes >> 1) << " clocks per pass "; \
x::reset(); \
}
#define series(n) \
{ if (do_test) test(n); if (do_time) time(n, 1); if (do_time) time(n, 2); \
if (do_time) time(n, 3); if (do_time) time(n, 4); if (do_time) time(n, 5); \
if (do_time) time(n, 6); if (do_time) time(n, 7); if (do_time) time(n, 8); \
if (do_time) time(n, 9); if (do_time) time(n, 10); }
int N1 = 1, N2 = 500000000, NM = INT_MAX;
int mult = 1; // used to stay under timelimit on ideone
unsigned long long k = 0;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
bool do_time = 1, do_test = 1;
bool passed = true;
#ifdef HOPMAN_FAST
series(hopman_fast)
#endif
#ifdef WM_VEC
series(wm::vec)
#endif
#ifdef TM_CPP
series(tmn::cpp)
#endif
#ifdef TM_VEC
series(tmn::vec)
#endif
#ifdef AK_UNROLLED
series(ak::unrolled)
#endif
#if defined(AK_BW)
series(ak::bw)
#endif
#if defined(AK_FW)
series(ak::fw)
#endif
return k;
}
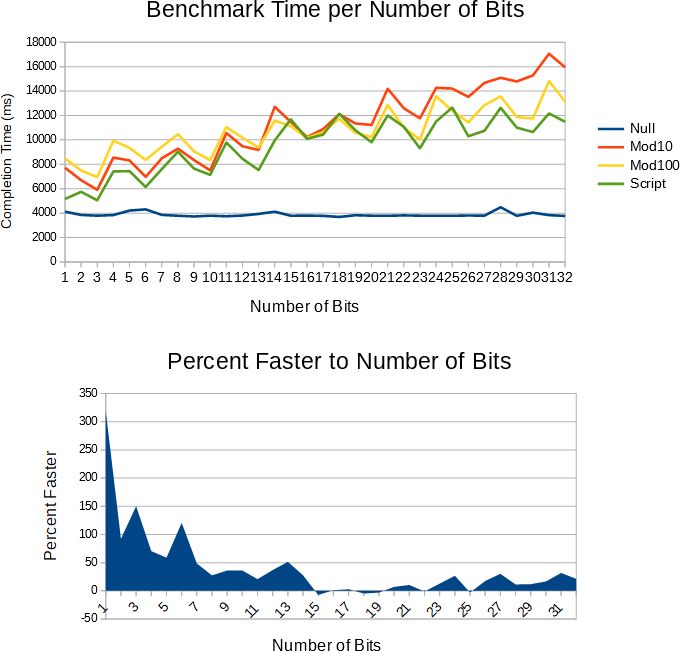
整数から文字列への最速のアルゴリズムを作成したと思います。これはModulo 100アルゴリズムのバリエーションであり、約33%高速です。最も重要なことは、小さい数値でも大きい数値でも高速です。スクリプトItoSアルゴリズムと呼ばれます。私がアルゴリズムをどのように設計したかを説明する論文を読むには@see https://github.com/kabuki-starship/kabuki-toolkit/wiki/Engineering-a-Faster-Integer-to-String-Algorithm =。アルゴリズムを使用することもできますが、 Kabuki VM に貢献することを検討し、 Script ;を確認してください。特に、AMIL-NLPやソフトウェア定義のネットワークプロトコルに興味がある場合。
/** Kabuki Toolkit
@version 0.x
@file ~/source/crabs/print_itos.cc
@author Cale McCollough <[email protected]>
@license Copyright (C) 2017-2018 Cale McCollough <[email protected]>;
All right reserved (R). Licensed under the Apache License, Version
2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in
compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License
[here](http://www.Apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0). Unless
required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
implied. See the License for the specific language governing
permissions and limitations under the License.
*/
#include <stdafx.h>
#include "print_itos.h"
#if MAJOR_SEAM >= 1 && MINOR_SEAM >= 1
#if MAJOR_SEAM == 1 && MINOR_SEAM == 1
#define DEBUG 1
#define PRINTF(format, ...) printf(format, __VA_ARGS__);
#define PUTCHAR(c) putchar(c);
#define PRINT_PRINTED\
sprintf_s (buffer, 24, "%u", value); *text_end = 0;\
printf ("\n Printed \"%s\" leaving value:\"%s\":%u",\
begin, buffer, (uint)strlen (buffer));
#define PRINT_BINARY PrintBinary (value);
#define PRINT_BINARY_TABLE PrintBinaryTable (value);
#else
#define PRINTF(x, ...)
#define PUTCHAR(c)
#define PRINT_PRINTED
#define PRINT_BINARY
#define PRINT_BINARY_TABLE
#endif
namespace _ {
void PrintLine (char c) {
std::cout << '\n';
for (int i = 80; i > 0; --i)
std::cout << c;
}
char* Print (uint32_t value, char* text, char* text_end) {
// Lookup table for powers of 10.
static const uint32_t k10ToThe[]{
1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000, 10000000, 100000000,
1000000000, ~(uint32_t)0 };
/** Lookup table of ASCII char pairs for 00, 01, ..., 99.
To convert this algorithm to big-endian, flip the digit pair bytes. */
static const uint16_t kDigits00To99[100] = {
0x3030, 0x3130, 0x3230, 0x3330, 0x3430, 0x3530, 0x3630, 0x3730, 0x3830,
0x3930, 0x3031, 0x3131, 0x3231, 0x3331, 0x3431, 0x3531, 0x3631, 0x3731,
0x3831, 0x3931, 0x3032, 0x3132, 0x3232, 0x3332, 0x3432, 0x3532, 0x3632,
0x3732, 0x3832, 0x3932, 0x3033, 0x3133, 0x3233, 0x3333, 0x3433, 0x3533,
0x3633, 0x3733, 0x3833, 0x3933, 0x3034, 0x3134, 0x3234, 0x3334, 0x3434,
0x3534, 0x3634, 0x3734, 0x3834, 0x3934, 0x3035, 0x3135, 0x3235, 0x3335,
0x3435, 0x3535, 0x3635, 0x3735, 0x3835, 0x3935, 0x3036, 0x3136, 0x3236,
0x3336, 0x3436, 0x3536, 0x3636, 0x3736, 0x3836, 0x3936, 0x3037, 0x3137,
0x3237, 0x3337, 0x3437, 0x3537, 0x3637, 0x3737, 0x3837, 0x3937, 0x3038,
0x3138, 0x3238, 0x3338, 0x3438, 0x3538, 0x3638, 0x3738, 0x3838, 0x3938,
0x3039, 0x3139, 0x3239, 0x3339, 0x3439, 0x3539, 0x3639, 0x3739, 0x3839,
0x3939, };
static const char kMsbShift[] = { 4, 7, 11, 14, 17, 21, 24, 27, 30, };
if (!text) {
return nullptr;
}
if (text >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
uint16_t* text16;
char digit;
uint32_t scalar;
uint16_t digits1and2,
digits3and4,
digits5and6,
digits7and8;
uint32_t comparator;
#if MAJOR_SEAM == 1 && MINOR_SEAM == 1
// Write a bunches of xxxxxx to the buffer for debug purposes.
for (int i = 0; i <= 21; ++i) {
*(text + i) = 'x';
}
*(text + 21) = 0;
char* begin = text;
char buffer[256];
#endif
if (value < 10) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[0, 9] length:1 ")
if (text + 1 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '0' + (char)value;
PRINT_PRINTED
return text;
}
if (value < 100) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10, 99] length:2 ")
if (text + 2 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text) = kDigits00To99[value];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 2;
}
if (value >> 14) {
if (value >> 27) {
if (value >> 30) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1073741824, 4294967295] length:10")
Print10:
if (text + 10 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
comparator = 100000000;
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)(value / comparator);
PRINTF ("\n digits1and2:%u", digits1and2)
value -= digits1and2 * comparator;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
text += 2;
goto Print8;
}
else {
comparator = 1000000000;
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100000000, 1073741823] length:10")
goto Print10;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[134217727, 999999999] length:9")
if (text + 9 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
comparator = 100000000;
digit = (char)(value / comparator);
*text++ = digit + '0';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator * digit;
goto Print8;
}
}
else if (value >> 24) {
comparator = k10ToThe[8];
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100000000, 134217728] length:9")
if (text + 9 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[16777216, 9999999] length:8")
if (text + 8 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
Print8:
PRINTF ("\n Print8:")
scalar = 10000;
digits5and6 = (uint16_t)(value / scalar);
digits1and2 = value - scalar * digits5and6;
digits7and8 = digits5and6 / 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / 100;
digits5and6 -= 100 * digits7and8;
digits1and2 -= 100 * digits3and4;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 6) =
kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 4) =
kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2) =
kDigits00To99[digits5and6];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text) =
kDigits00To99[digits7and8];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 8;
}
else if (value >> 20) {
comparator = 10000000;
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10000000, 16777215] length:8")
if (text + 8 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator;
}
else {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1048576, 9999999] length:7")
if (text + 7 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
}
scalar = 10000;
digits5and6 = (uint16_t)(value / scalar);
digits1and2 = value - scalar * digits5and6;
digits7and8 = digits5and6 / 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / 100;
digits5and6 -= 100 * digits7and8;
digits1and2 -= 100 * digits3and4;;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 5) =
kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 3) =
kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 1) =
kDigits00To99[digits5and6];
PRINT_PRINTED
*text = (char)digits7and8 + '0';
return text + 7;
}
else if (value >> 17) {
comparator = 1000000;
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100000, 1048575] length:7")
if (text + 7 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator;
}
else {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[131072, 999999] length:6")
if (text + 6 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
}
Print6:
scalar = 10000;
digits5and6 = (uint16_t)(value / scalar);
digits1and2 = value - scalar * digits5and6;
digits7and8 = digits5and6 / 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / 100;
digits5and6 -= 100 * digits7and8;
digits1and2 -= 100 * digits3and4;
text16 = reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 6);
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 4) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2) = kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text ) = kDigits00To99[digits5and6];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 6;
}
else { // (value >> 14)
if (value >= 100000) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[65536, 131071] length:6")
goto Print6;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10000, 65535] length:5")
if (text + 5 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
digits5and6 = 10000;
digit = (uint8_t)(value / digits5and6);
value -= digits5and6 * digit;
*text = digit + '0';
PRINT_PRINTED
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)value;
digits5and6 = 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / digits5and6;
digits1and2 -= digits3and4 * digits5and6;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 1) =
kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
PRINTF ("\n digits1and2:%u", digits1and2)
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 3) =
kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 5;
}
}
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)value;
if (value >> 10) {
digits5and6 = 10000;
if (digits1and2 >= digits5and6) {
if (text + 5 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10000, 16383] length:5")
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
digits1and2 -= digits5and6;
}
else {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1024, 9999] length:4")
if (text + 4 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
}
digits5and6 = 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / digits5and6;
digits1and2 -= digits3and4 * digits5and6;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text ) = kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 4;
}
else {
if (text + 4 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
digits3and4 = 1000;
if (digits1and2 >= digits3and4) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1000, 1023] length:4")
digits1and2 -= digits3and4;
text16 = reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2);
*text16-- = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*text16 = (((uint16_t)'1') | (((uint16_t)'0') << 8));
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 4;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100, 999] length:3")
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)value;
digits3and4 = 100;
digit = (char)(digits1and2 / digits3and4);
digits1and2 -= digit * digits3and4;
*text = digit + '0';
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 1) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 3;
}
}
} //< namespace _
#undef PRINTF
#undef PRINT_PRINTED
#endif //< MAJOR_SEAM >= 1 && MINOR_SEAM >= 1
著者
次のコードを使用します(MSVCの場合):
テンプレート化されたtBitScanReverse:
#include <intrin.h>
namespace intrin {
#pragma intrinsic(_BitScanReverse)
#pragma intrinsic(_BitScanReverse64)
template<typename TIntegerValue>
__forceinline auto tBitScanReverse(DWORD * out_index, TIntegerValue mask)
-> std::enable_if_t<(std::is_integral<TIntegerValue>::value && sizeof(TIntegerValue) == 4), unsigned char>
{
return _BitScanReverse(out_index, mask);
}
template<typename TIntegerValue>
__forceinline auto tBitScanReverse(DWORD * out_index, TIntegerValue mask)
-> std::enable_if_t<(std::is_integral<TIntegerValue>::value && sizeof(TIntegerValue) == 8), unsigned char>
{
#if !(_M_IA64 || _M_AMD64)
auto res = _BitScanReverse(out_index, (unsigned long)(mask >> 32));
if (res) {
out_index += 32;
return res;
}
return _BitScanReverse(out_index, (unsigned long)mask);
#else
return _BitScanReverse64(out_index, mask);
#endif
}
}
char/wchar_tヘルパー:
template<typename TChar> inline constexpr TChar ascii_0();
template<> inline constexpr char ascii_0() { return '0'; }
template<> inline constexpr wchar_t ascii_0() { return L'0'; }
template<typename TChar, typename TInt> inline constexpr TChar ascii_DEC(TInt d) { return (TChar)(ascii_0<TChar>() + d); }
10のテーブルのべき乗:
static uint32 uint32_powers10[] = {
1,
10,
100,
1000,
10000,
100000,
1000000,
10000000,
100000000,
1000000000
// 123456789
};
static uint64 uint64_powers10[] = {
1ULL,
10ULL,
100ULL,
1000ULL,
10000ULL,
100000ULL,
1000000ULL,
10000000ULL,
100000000ULL,
1000000000ULL,
10000000000ULL,
100000000000ULL,
1000000000000ULL,
10000000000000ULL,
100000000000000ULL,
1000000000000000ULL,
10000000000000000ULL,
100000000000000000ULL,
1000000000000000000ULL,
10000000000000000000ULL
// 1234567890123456789
};
template<typename TUint> inline constexpr const TUint * powers10();
template<> inline constexpr const uint32 * powers10() { return uint32_powers10; }
template<> inline constexpr const uint64 * powers10() { return uint64_powers10; }
実際の印刷:
template<typename TChar, typename TUInt>
__forceinline auto
print_dec(
TUInt u,
TChar * & buffer) -> typename std::enable_if_t<std::is_unsigned<TUInt>::value>
{
if (u < 10) { // 1-digit, including 0
*buffer++ = ascii_DEC<TChar>(u);
}
else {
DWORD log2u;
intrin::tBitScanReverse(&log2u, u); // log2u [3,31] (u >= 10)
DWORD log10u = ((log2u + 1) * 77) >> 8; // log10u [1,9] 77/256 = ln(2) / ln(10)
DWORD digits = log10u + (u >= powers10<TUInt>()[log10u]); // digits [2,10]
buffer += digits;
auto p = buffer;
for (--digits; digits; --digits) {
auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10;
*--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d);
u = x;
}
*--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(u);
}
}
最後のループは展開できます:
switch (digits) {
case 10: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 9: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 8: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 7: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 6: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 5: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 4: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 3: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 2: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(u); break; }
default: __assume(0);
}
主なアイデアは、以前に提案された@atlasteと同じです: https://stackoverflow.com/a/29039967/2204001
最近の活動のためにこれに出くわしました。ベンチマークを追加する時間はあまりありませんが、高速整数から文字列への変換が必要なときに過去に書いたものを追加したかったのです...
https://github.com/CarloWood/ai-utils/blob/master/itoa.h
https://github.com/CarloWood/ai-utils/blob/master/itoa.cxx
ここで使用されるトリックは、ユーザーが(スタック上に)十分に大きいstd :: arrayを提供する必要があり、このコードが文字列を逆方向に書き込み、ユニットから開始し、オフセット付きの配列にポインターを返すことです結果が実際に始まる場所に。
したがって、これはメモリを割り当てたり移動したりしませんが、結果の桁ごとに除算とモジュロが必要です(CPUで内部的に実行されるコードであるため、十分に高速であると考えています。通常、メモリアクセスは問題です)。
User434507のソリューションの変更。 C++文字列の代わりに文字配列を使用するように変更されました。少し速くなります。また、コードの0のチェックを下に移動しました。これは私の特定のケースでは決して起こらないからです。それがあなたの場合により一般的であるならば、それを後ろに動かしてください。
// Int2Str.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "StopWatch.h"
using namespace std;
const char digit_pairs[201] = {
"00010203040506070809"
"10111213141516171819"
"20212223242526272829"
"30313233343536373839"
"40414243444546474849"
"50515253545556575859"
"60616263646566676869"
"70717273747576777879"
"80818283848586878889"
"90919293949596979899"
};
void itostr(int n, char* c) {
int sign = -(n<0);
unsigned int val = (n^sign)-sign;
int size;
if(val>=10000) {
if(val>=10000000) {
if(val>=1000000000) {
size=10;
}
else if(val>=100000000) {
size=9;
}
else size=8;
}
else {
if(val>=1000000) {
size=7;
}
else if(val>=100000) {
size=6;
}
else size=5;
}
}
else {
if(val>=100) {
if(val>=1000) {
size=4;
}
else size=3;
}
else {
if(val>=10) {
size=2;
}
else if(n==0) {
c[0]='0';
c[1] = '\0';
return;
}
else size=1;
}
}
size -= sign;
if(sign)
*c='-';
c += size-1;
while(val>=100) {
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0) {
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
c[size+1] = '\0';
}
void itostr(unsigned val, char* c)
{
int size;
if(val>=10000)
{
if(val>=10000000)
{
if(val>=1000000000)
size=10;
else if(val>=100000000)
size=9;
else
size=8;
}
else
{
if(val>=1000000)
size=7;
else if(val>=100000)
size=6;
else
size=5;
}
}
else
{
if(val>=100)
{
if(val>=1000)
size=4;
else
size=3;
}
else
{
if(val>=10)
size=2;
else if (val==0) {
c[0]='0';
c[1] = '\0';
return;
}
else
size=1;
}
}
c += size-1;
while(val>=100)
{
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0)
{
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
c[size+1] = '\0';
}
void test() {
bool foundmismatch = false;
char str[16];
char compare[16];
for(int i = -1000000; i < 1000000; i++) {
int random = Rand();
itostr(random, str);
itoa(random, compare, 10);
if(strcmp(str, compare) != 0) {
cout << "Mismatch found: " << endl;
cout << "Generated: " << str << endl;
cout << "Reference: " << compare << endl;
foundmismatch = true;
}
}
if(!foundmismatch) {
cout << "No mismatch found!" << endl;
}
cin.get();
}
void benchmark() {
StopWatch stopwatch;
stopwatch.setup("Timer");
stopwatch.reset();
stopwatch.start();
char str[16];
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < 2000000; i++) {
itostr(i, str);
}
stopwatch.stop();
cin.get();
}
int main( int argc, const char* argv[]) {
benchmark();
}