文字列内の文字のn番目の出現を見つける方法は?
here に投稿された質問と同様に、Javaで解決策を探しています。
つまり、文字列から文字/文字列のn番目の出現のインデックスを見つける方法は?
例: "/ folder1/folder2/folder3 /"。この場合、スラッシュ(/)の3番目の出現を要求すると、folder3の前に表示され、このインデックス位置を返すことを期待しています。私の実際の意図は、文字のn番目の出現からサブストリング化することです。
Java APIで使用できる便利な/すぐに使用できるメソッドはありますか、またはこれを解決するために独自の小さなロジックを記述する必要がありますか?
また、
- Apache Commons Langの StringUtils で、この目的でサポートされているメソッドがあるかどうかをすばやく検索しましたが、見つかりませんでした。
- この点で正規表現は役立ちますか?
プロジェクトがすでにApache Commonsに依存している場合は、 StringUtils.ordinalIndexOf を使用できます。
public static int ordinalIndexOf(String str, String substr, int n) {
int pos = str.indexOf(substr);
while (--n > 0 && pos != -1)
pos = str.indexOf(substr, pos + 1);
return pos;
}
この投稿は記事として書き直されました here 。
N番目の文字列の出現を見つける最も簡単な解決策は、Apache Commonsの StringUtils.ordinalIndexOf() を使用することだと思います。
例:
StringUtils.ordinalIndexOf("aabaabaa", "b", 2) == 5
2つの単純なオプションが発生します。
charAt()を繰り返し使用するindexOf()を繰り返し使用する
例えば:
public static int nthIndexOf(String text, char needle, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < text.length(); i++)
{
if (text.charAt(i) == needle)
{
n--;
if (n == 0)
{
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
それはindexOfを繰り返し使用するのと同じくらいうまく機能しないかもしれませんが、正しくする方が簡単かもしれません。
次のようなものを試すことができます:
import Java.util.regex.Matcher;
import Java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(from3rd("/folder1/folder2/folder3/"));
}
private static Pattern p = Pattern.compile("(/[^/]*){2}/([^/]*)");
public static String from3rd(String in) {
Matcher m = p.matcher(in);
if (m.matches())
return m.group(2);
else
return null;
}
}
正規表現でいくつかの仮定を行ったことに注意してください。
- 入力パスは絶対パスです(つまり、「/」で始まります)。
- 結果に3番目の「/」は必要ありません。
コメントで要求されたように、正規表現の説明を試みます:(/[^/]*){2}/([^/]*)
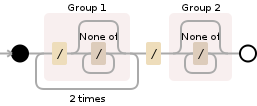
/[^/]*は/に続いて[^/]*(/ではない任意の数の文字)、(/[^/]*)は、前の式を単一のエンティティにグループ化します。これは、式の1stグループです。(/[^/]*){2}は、グループが{2}回完全に一致する必要があることを意味します。[^/]*は、/ではない任意の数の文字です。([^/]*)は、前の表現を単一のエンティティにグループ化します。これは、式の2ndグループです。
この方法では、2番目のグループに一致するサブストリングを取得するだけで済みます:return m.group(2);
画像提供: Debuggex
Aioobeの回答にいくつか変更を加えて、n番目のlastIndexOfバージョンを取得し、NPEの問題を修正しました。以下のコードを参照してください:
public int nthLastIndexOf(String str, char c, int n) {
if (str == null || n < 1)
return -1;
int pos = str.length();
while (n-- > 0 && pos != -1)
pos = str.lastIndexOf(c, pos - 1);
return pos;
}
public static int nth(String source, String pattern, int n) {
int i = 0, pos = 0, tpos = 0;
while (i < n) {
pos = source.indexOf(pattern);
if (pos > -1) {
source = source.substring(pos+1);
tpos += pos+1;
i++;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
return tpos - 1;
}
現在、Apache Commons Langの StringUtils のISサポートがあります。
これはプリミティブです:
int org.Apache.commons.lang.StringUtils.ordinalIndexOf(CharSequence str, CharSequence searchStr, int ordinal)
あなたの問題のために、次のコードを書くことができます:StringUtils.ordinalIndexOf(uri, "/", 3)
lastOrdinalIndexOf メソッドを使用して、文字列内の文字の最後のn番目の出現を検索することもできます。
別のアプローチ:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "/folder1/folder2/folder3/";
int index = nthOccurrence(str, '/', 3);
System.out.println(index);
}
public static int nthOccurrence(String s, char c, int occurrence) {
return nthOccurrence(s, 0, c, 0, occurrence);
}
public static int nthOccurrence(String s, int from, char c, int curr, int expected) {
final int index = s.indexOf(c, from);
if(index == -1) return -1;
return (curr + 1 == expected) ? index :
nthOccurrence(s, index + 1, c, curr + 1, expected);
}
この答えは@aioobeの答えを改善します。その答えの2つのバグが修正されました。
1。 n = 0は-1を返すはずです。
2。 n番目のオカレンスは-1を返しましたが、n-1番目のオカレンスで機能しました。
これを試して !
public int nthOccurrence(String str, char c, int n) {
if(n <= 0){
return -1;
}
int pos = str.indexOf(c, 0);
while (n-- > 1 && pos != -1)
pos = str.indexOf(c, pos+1);
return pos;
}
public class Sam_Stringnth {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="abcabcabc";
int n = nthsearch(str, 'c', 3);
if(n<=0)
System.out.println("Character not found");
else
System.out.println("Position is:"+n);
}
public static int nthsearch(String str, char ch, int n){
int pos=0;
if(n!=0){
for(int i=1; i<=n;i++){
pos = str.indexOf(ch, pos)+1;
}
return pos;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
}
これは、String.split(..)メソッドでも実現できます。
String str = "";
String[] tokens = str.split("/")
return tokens[nthIndex] == null
public static int findNthOccurrence(String phrase, String str, int n)
{
int val = 0, loc = -1;
for(int i = 0; i <= phrase.length()-str.length() && val < n; i++)
{
if(str.equals(phrase.substring(i,i+str.length())))
{
val++;
loc = i;
}
}
if(val == n)
return loc;
else
return -1;
}
このコードは、n番目のオカレンス位置のサブストリング、つまりフィールド幅を返します。例。文字列"low melowでのスタックオーバーフロー"が検索する文字列である場合2ndトークン "low"の発生"18 and 21"。 indexOfOccurance( "Stack melow in low melow"、low、2)は、文字列で18と21を返します。
class Example{
public Example(){
}
public String indexOfOccurance(String string, String token, int nthOccurance) {
int lengthOfToken = token.length();
int nthCount = 0;
for (int shift = 0,count = 0; count < string.length() - token.length() + 2; count++, shift++, lengthOfToken++)
if (string.substring(shift, lengthOfToken).equalsIgnoreCase(token)) {
// keeps count of nthOccurance
nthCount++;
if (nthCount == nthOccurance){
//checks if nthCount == nthOccurance. If true, then breaks
return String.valueOf(shift)+ " " +String.valueOf(lengthOfToken);
}
}
return "-1";
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Example example = new Example();
String string = "the man, the woman and the child";
int nthPositionOfThe = 3;
System.out.println("3rd Occurance of the is at " + example.indexOfOccurance(string, "the", nthPositionOfThe));
}
}
私の解決策:
/**
* Like String.indexOf, but find the n:th occurance of c
* @param s string to search
* @param c character to search for
* @param n n:th character to seach for, starting with 1
* @return the position (0-based) of the found char, or -1 if failed
*/
public static int nthIndexOf(String s, char c, int n) {
int i = -1;
while (n-- > 0) {
i = s.indexOf(c, i + 1);
if (i == -1)
break;
}
return i;
}
/* program to find nth occurence of a character */
import Java.util.Scanner;
public class CharOccur1
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
Scanner scr=new Scanner(System.in);
int position=-1,count=0;
System.out.println("enter the string");
String str=scr.nextLine();
System.out.println("enter the nth occurence of the character");
int n=Integer.parseInt(scr.next());
int leng=str.length();
char c[]=new char[leng];
System.out.println("Enter the character to find");
char key=scr.next().charAt(0);
c=str.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<c.length;i++)
{
if(c[i]==key)
{
count++;
position=i;
if(count==n)
{
System.out.println("Character found");
System.out.println("the position at which the " + count + " ocurrence occurs is " + position);
return;
}
}
}
if(n>count)
{
System.out.println("Character occurs "+ count + " times");
return;
}
}
}